Description
What is a battery jar?
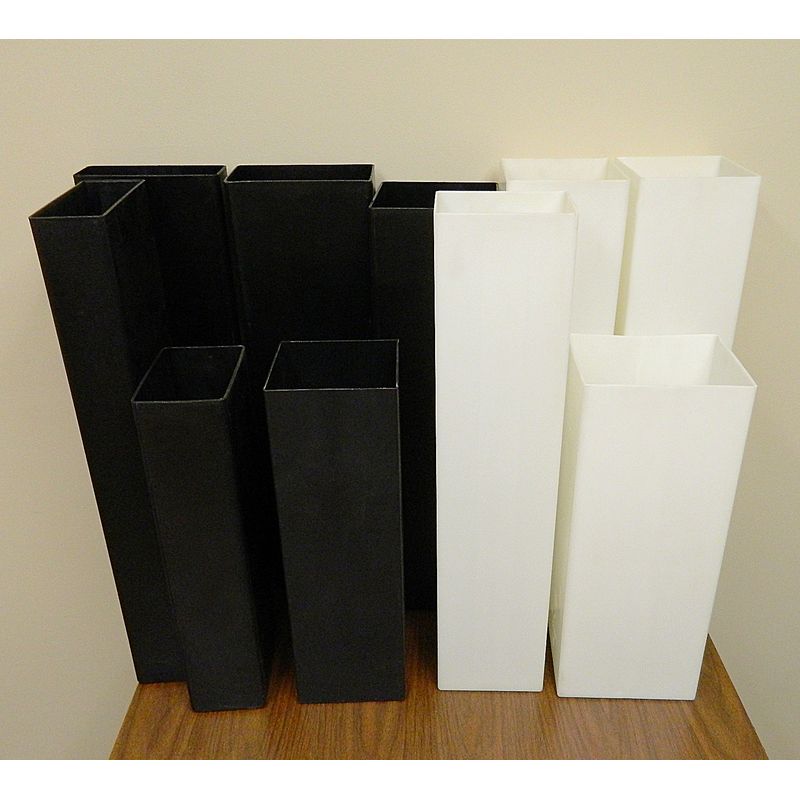
A battery jar is one component that battery makers use to form a lead-acid battery. As the name implies, battery jars were originally made of glass. Modern battery jars are made of plastic such as polypropylene or polyethylene since they are not affected by battery acid. The most common size jars range from 5-plate to 33-plate batteries. They are made by several companies in different heights up to 34″ or more. This jar is also referred to a battery container or battery case.
What other parts are needed to make a battery?
The main component is the set of positive and negative lead plates. The acid reacts with the plates to generate electricity. The other components may vary depending on the manufacturer and battery type, but here is a list of the most common ones.
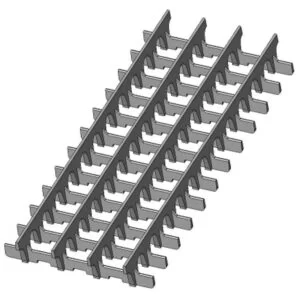
Battery Bridge Rest
The bridge rest is placed on the bottom of the jar to support the lead plates. In all lead-acid batteries, small particles form which fall to the bottom. After this debris accumulates and builds up against the lead plates, this will likely cause a short circuit and ruin the battery. For this reason, a bridge rest acts as a spacer to make room for the debris to settle below the plates. This extends the life of the battery by preventing short circuits.
Battery Element Protector
In like manner, an element protector, also called a moss guard, has the same role. It is placed on top of the lead plates to block debris from forming a layer across the plates, thus stopping short circuits.
Battery Edge Protector
The edge protector is placed on the top edge of single lead plates to guard them against damage during assembly. It also covers the top edge and helps to prevent shorts.
Battery Cell Cover
The battery cell cover is welded to the top of the jar, forming a leak-proof seal. The lead bushings on the cover are then soldered to the battery posts.
Floating Battery Post Bushing
Over time, the positive post expands and grows upward. This growth would damage the cover if the lead post is affixed to the battery cell cover. The floating bushing stops any damage by moving upward at the same rate as the post. To prevent leakage, the two O-rings on the bushing maintain the seal against the cover.
Battery Vent Caps
All lead-acid batteries generate gas, especially when they are being charged. This gas will build up pressure and cause damage to the battery unless it can escape. A vent cap prevents this issue by allowing the gas to exit from the battery. The best ones contain a flame arrestor which prevents the gas inside the battery from igniting.
There are many types of vent caps. Some have a flame arrestor, and some do not. Other types such as Water Miser Battery Caps can slow the rate of water loss. Some vent caps must be removed from the battery so that more water can be added. Others have a flip-open top that lets them remain on the battery while checking the fluid level or adding water. A speed vent cap is made up of 3 or 4 vent caps that are all connected, thus letting you install or remove all of them simultaneously. Which type of vent cap you choose to buy depends on what options you need and on your budget. To help you choose, our FAQ page has a chart that shows our different models and their features.
What are lead-acid batteries used for?
Small batteries are mainly used in motorbikes and cars. Large deep-cycle batteries are used for a wide variety of applications including forklifts, golf carts, solar arrays, and more. They are used to provide backup power where a constant power source is needed.